

Next: Comparison between imaging techniques
Up: Validation and Comparison Between
Previous: Validation and Comparison Between
Automatic measurements of individual bifurcations were compared with manual
measurements for 17 randomly chosen bifurcations from red-free
retinal subimages.
Original images were collected with the
subjects seated throughout the study. The right pupil was dilated using
a topical mydriatic (1England). Retinal photographs were taken using a fundal camera with a 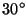 field of view (Kowa FX-50R, Kowa, Tokyo, Japan). For red-free images a green filter was
incorporated into the camera to enhance definition of retinal blood vessels. For fluorescein
images a fluorescein dye was previously injected intravenously.
Ilford FP4 (125 ASA) photographic film (Ilford Imaging UK Ltd., Knutsford,
England) was used. Only superior temporal views were analysed. Photographic
negatives were digitised using a
Nikon 35
field of view (Kowa FX-50R, Kowa, Tokyo, Japan). For red-free images a green filter was
incorporated into the camera to enhance definition of retinal blood vessels. For fluorescein
images a fluorescein dye was previously injected intravenously.
Ilford FP4 (125 ASA) photographic film (Ilford Imaging UK Ltd., Knutsford,
England) was used. Only superior temporal views were analysed. Photographic
negatives were digitised using a
Nikon 35 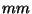 film scanner (LS-1000, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). Digitised images
were 2800 x 2400 pixels in size,
and segmented with an integer interval of
film scanner (LS-1000, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). Digitised images
were 2800 x 2400 pixels in size,
and segmented with an integer interval of
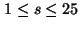 pixels.
Figure 12 shows some examples of the
individual bifurcations; (a - c) are the gray scale red-free subimages and (d - f)
are the automatic segmented and measured segments.
pixels.
Figure 12 shows some examples of the
individual bifurcations; (a - c) are the gray scale red-free subimages and (d - f)
are the automatic segmented and measured segments.
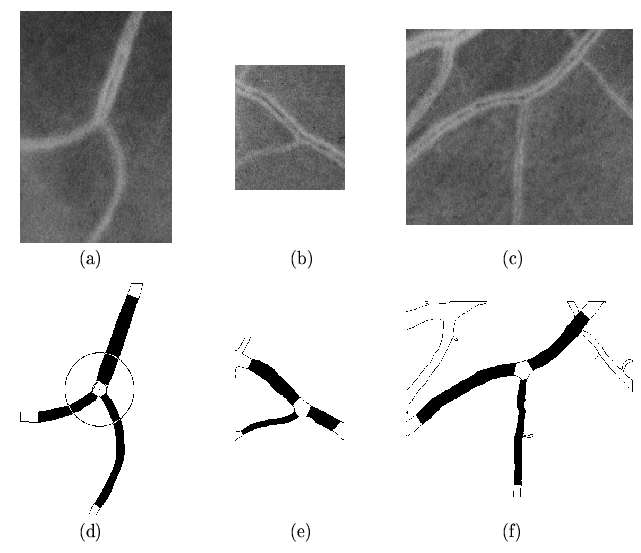
Figure 12:
Some examples of individual bifurcations in gray scale red-free images.
(a - c) are the original subimages and
(d - f) are the respective automatic segmented and measured segments.
(d) angles are measured along the skeleton lines within a distance from the
bifurcation point centre to a fixed circle.
Subimages are taken from gray scale images of size
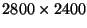 pixels.
pixels.
 |
The black areas in the segmented images represent the areas and lengths measured
per vessel segment,
an average diameter is calculated as 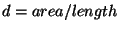 . Bifurcation angles,
. Bifurcation angles, 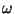 ,
were measured along the skeleton lines within a distance from the bifurcation centre
to a fixed circle
of
,
were measured along the skeleton lines within a distance from the bifurcation centre
to a fixed circle
of 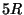 where
where 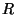 is the radius of
the maximum circle centered on the bifurcation point that fits inside the
boundary of the bifurcation,
as shown in Figure 12(d).
is the radius of
the maximum circle centered on the bifurcation point that fits inside the
boundary of the bifurcation,
as shown in Figure 12(d).
The skeleton of the vascular tree is obtained from the
segmented binary image by a thinning process where pixels are
eliminated from the boundaries towards the centre without destroying
connectivity in an 8-connected scheme [24].
A pruning process is applied to eliminate short, false spurs,
due to small undulations in the vessel boundary.
In the absence of a true measure, we defined a normalised
difference between measures 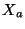 and
and 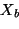 as:
as:
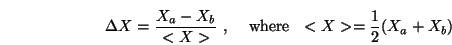 |
(9) |
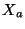 corresponds to automatic measurements and
corresponds to automatic measurements and 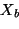 to manual [25].
Table I summarises the results.
to manual [25].
Table I summarises the results.
For  , automatic were smaller than manually measured diameters, whereas for
, automatic were smaller than manually measured diameters, whereas for
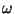 automatic were larger than manual angles.
Since the manual measurements
involved the average of 5 diameters measured close to the
bifurcation and the angles between straight lines fitted by eye,
these significant differences can not be taken as error but only as indications of
the variation between different measurement techniques.
automatic were larger than manual angles.
Since the manual measurements
involved the average of 5 diameters measured close to the
bifurcation and the angles between straight lines fitted by eye,
these significant differences can not be taken as error but only as indications of
the variation between different measurement techniques.


Next: Comparison between imaging techniques
Up: Validation and Comparison Between
Previous: Validation and Comparison Between
Elena Martínez
2003-05-16


![]() and
and ![]() as:
as:
![]() , automatic were smaller than manually measured diameters, whereas for
, automatic were smaller than manually measured diameters, whereas for
![]() automatic were larger than manual angles.
Since the manual measurements
involved the average of 5 diameters measured close to the
bifurcation and the angles between straight lines fitted by eye,
these significant differences can not be taken as error but only as indications of
the variation between different measurement techniques.
automatic were larger than manual angles.
Since the manual measurements
involved the average of 5 diameters measured close to the
bifurcation and the angles between straight lines fitted by eye,
these significant differences can not be taken as error but only as indications of
the variation between different measurement techniques.